 English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик
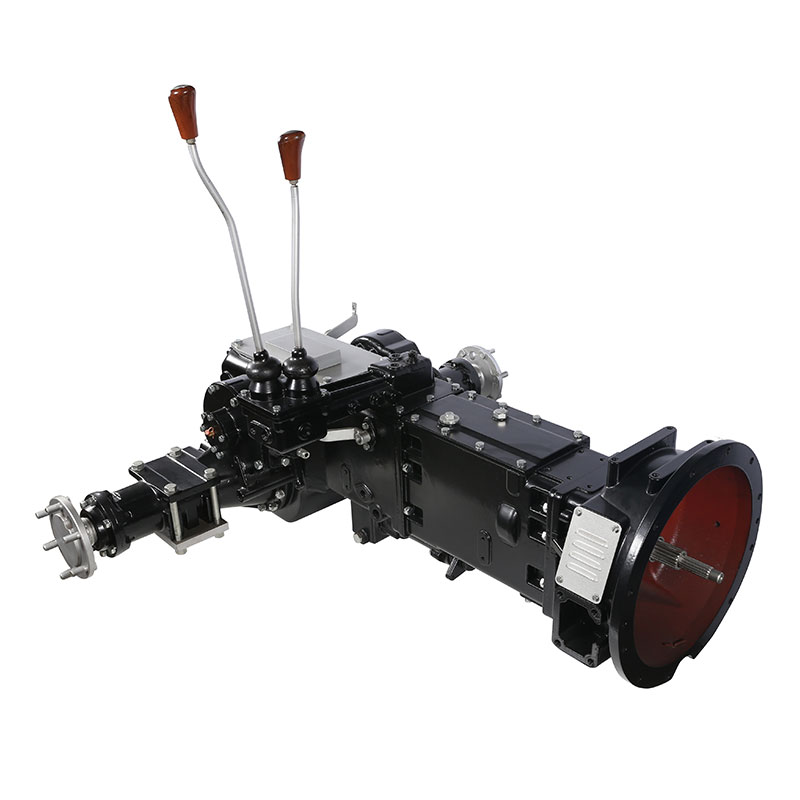
Flail Verge Mowers Gearbox
Send Inquiry
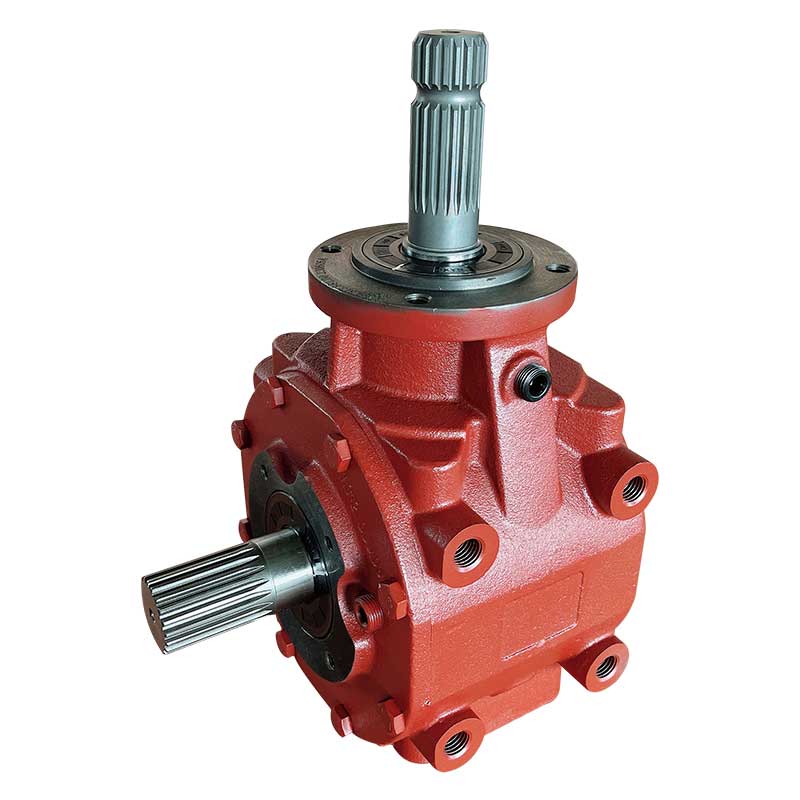
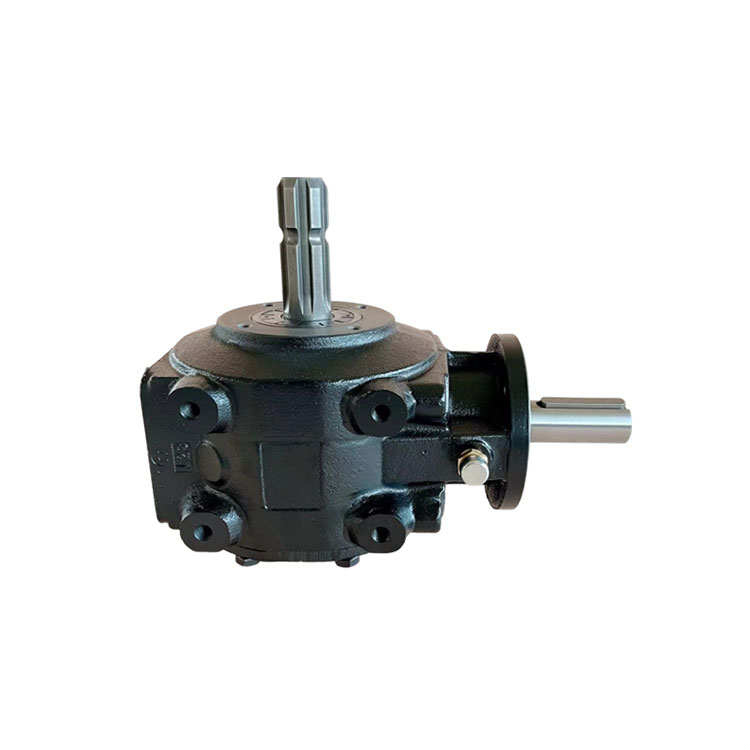
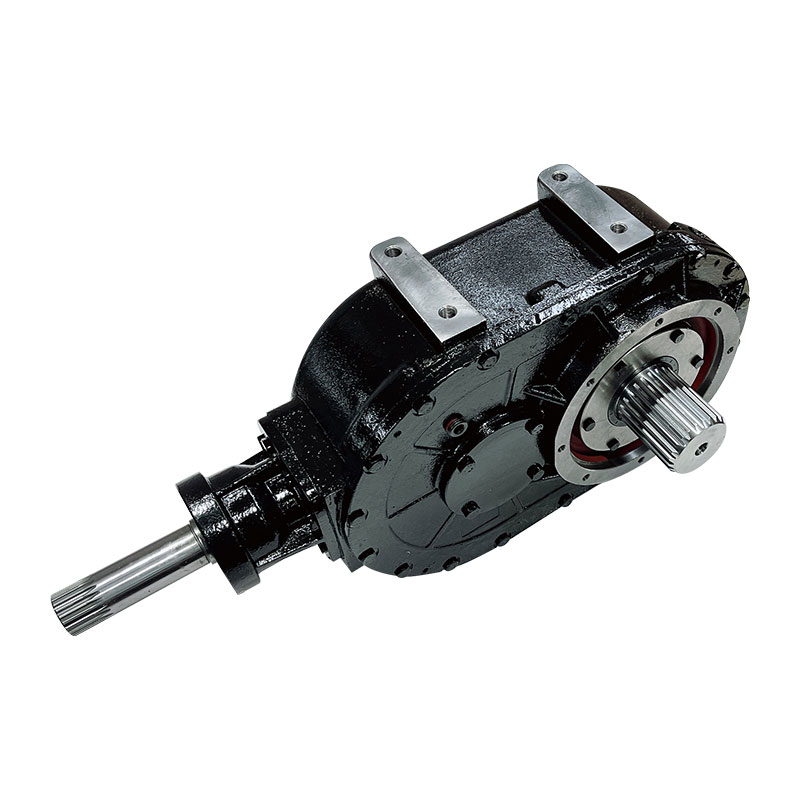
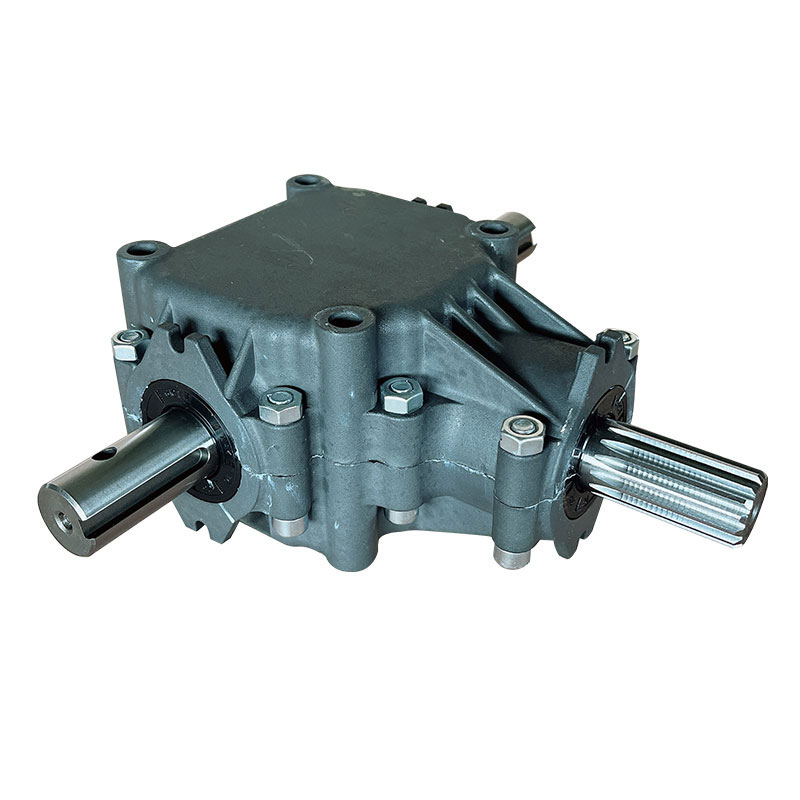
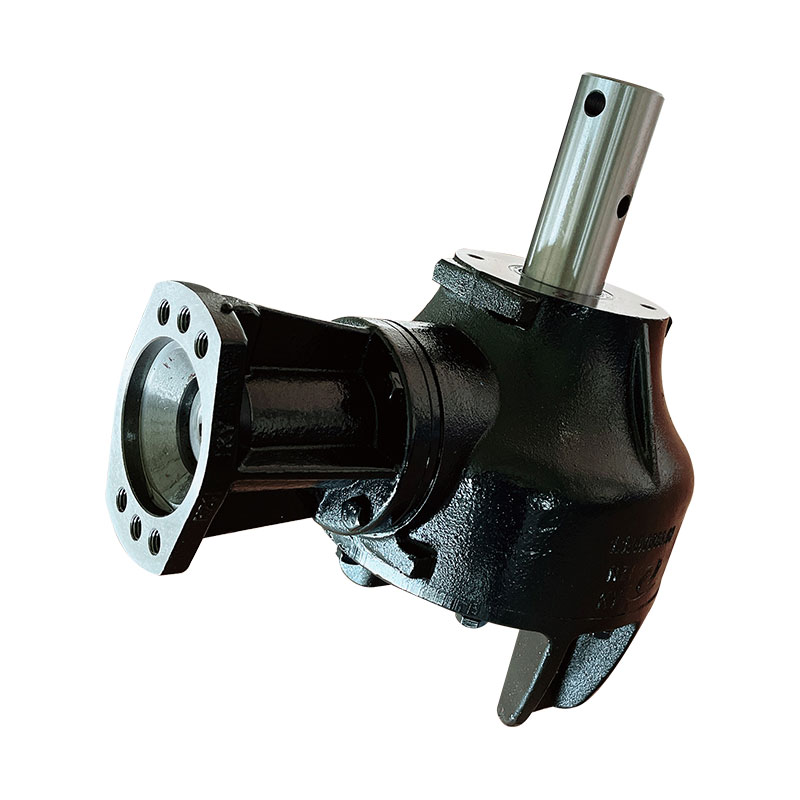
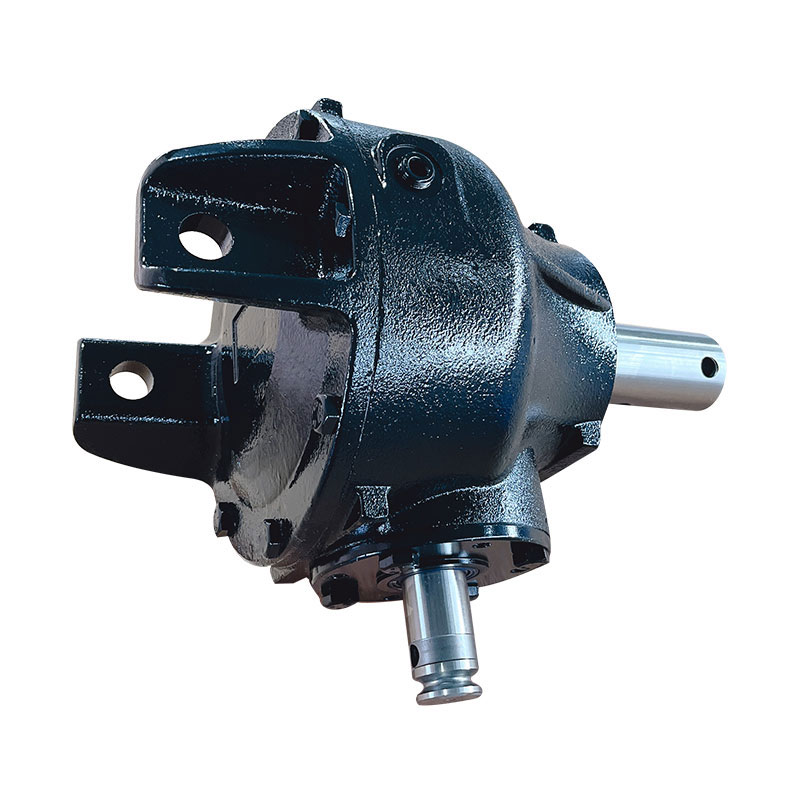
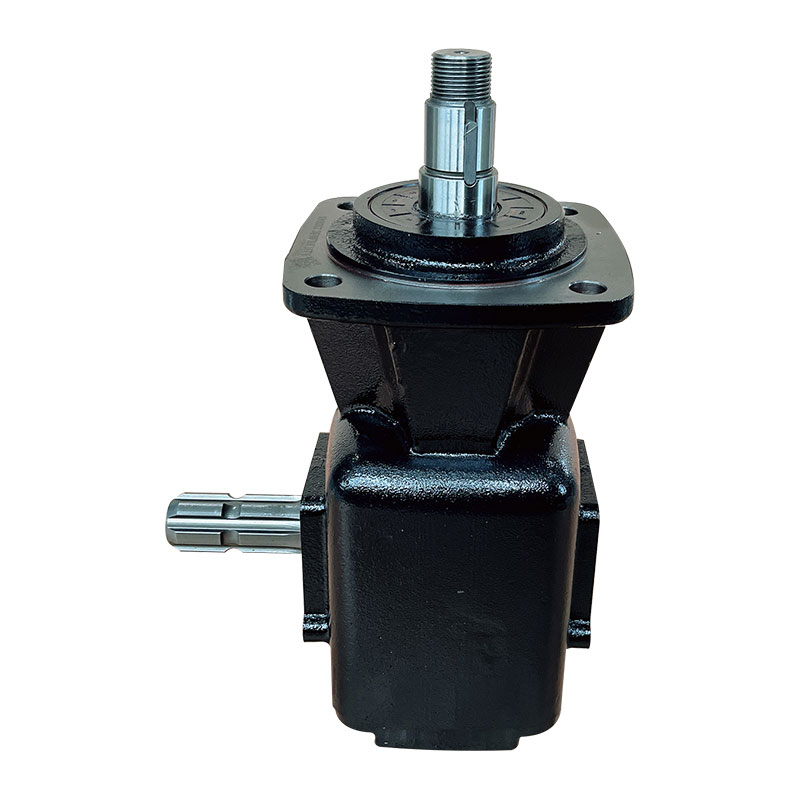
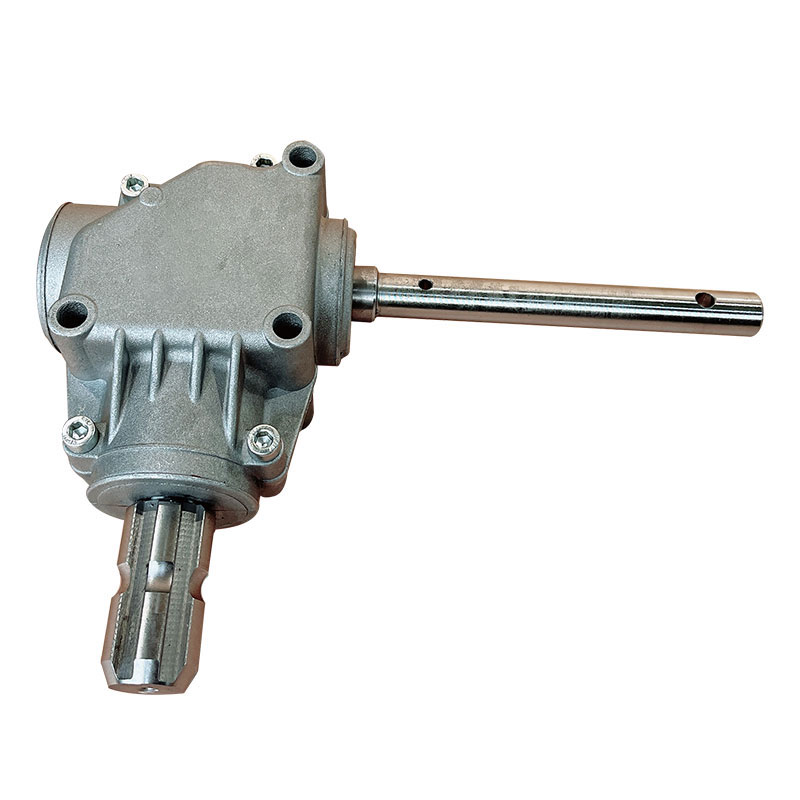
Flail Verge Mowers Gearbox
Flail verge mowers gearbox plays a crucial role in the functionality of flail verge mowers, which are used for cutting and maintaining vegetation along roadsides, embankments, ditches, and other hard-to-reach areas. The gearbox is responsible for transmitting power from the mower's engine to the flail cutting mechanism, converting rotational motion into the necessary cutting action.
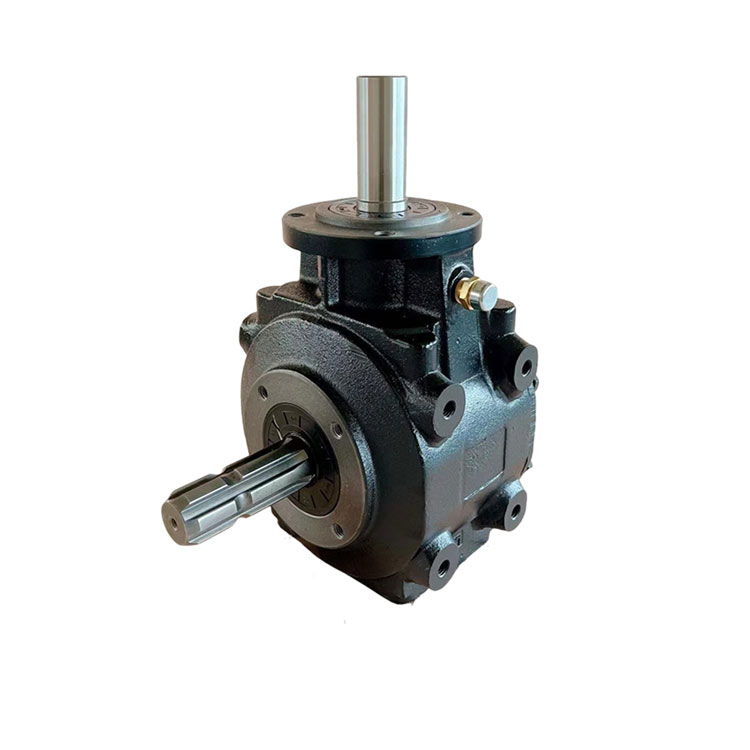
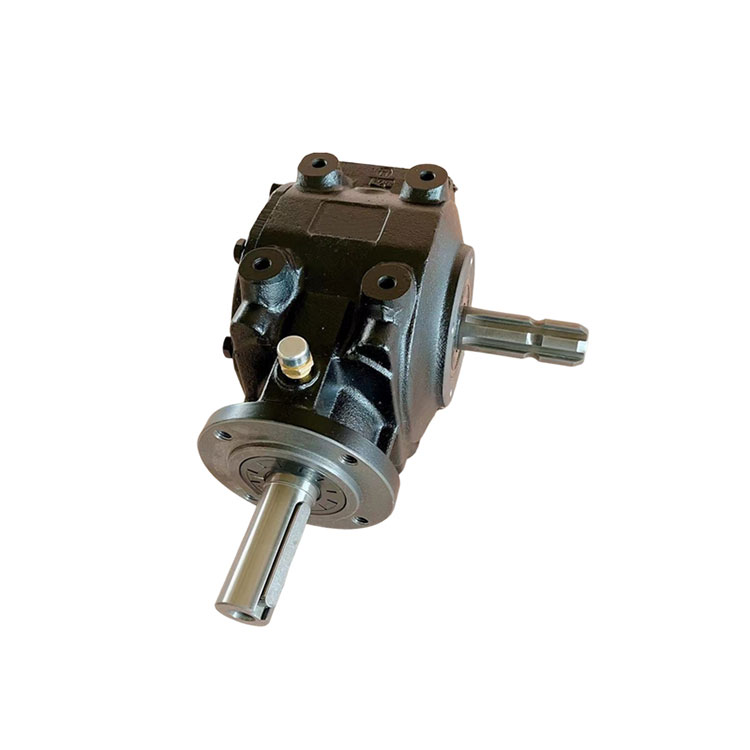
Flail verge Mowers gearbox data
|
Type of application |
Speed increasing unit |
|
Gear ratio |
3:1 |
|
Input speed |
540rpm |
|
Gearbox housing |
Ductile iron |
|
Input shaft |
6 teeth 1 3/8 spline shaft |
|
Output shaft |
Plain axis withkeyway |
|
Input power |
50Cv-36.8kw |
|
Weight |
23.2Kg |
|
Configuration |
Overrunning clutch available. |
|
Note |
Ship without oil |
Flail verge Mowers gearbox feature and application
Durability: Since flail verge mowers often operate in rugged environments and encounter tough vegetation, the gearbox must be built to withstand continuous use and potential impacts.
High torque capacity: The gearbox should be capable of handling high torque loads generated during the cutting process without sacrificing performance or risking damage.
Efficiency: A well-designed gearbox minimizes energy loss during power transmission, ensuring that the mower operates efficiently and effectively.

Flail verge Mowers gearbox details
The construction of a flail verge mower gearbox involves several key components that work together to transmit power from the mower's engine to the cutting mechanism. Here's a detailed overview of the typical construction of such a gearbox:
Housing: The gearbox housing serves as the outer casing that encloses and protects the internal components. It is typically made from sturdy materials such as cast iron or aluminum alloy to withstand the stresses and impacts encountered during operation.
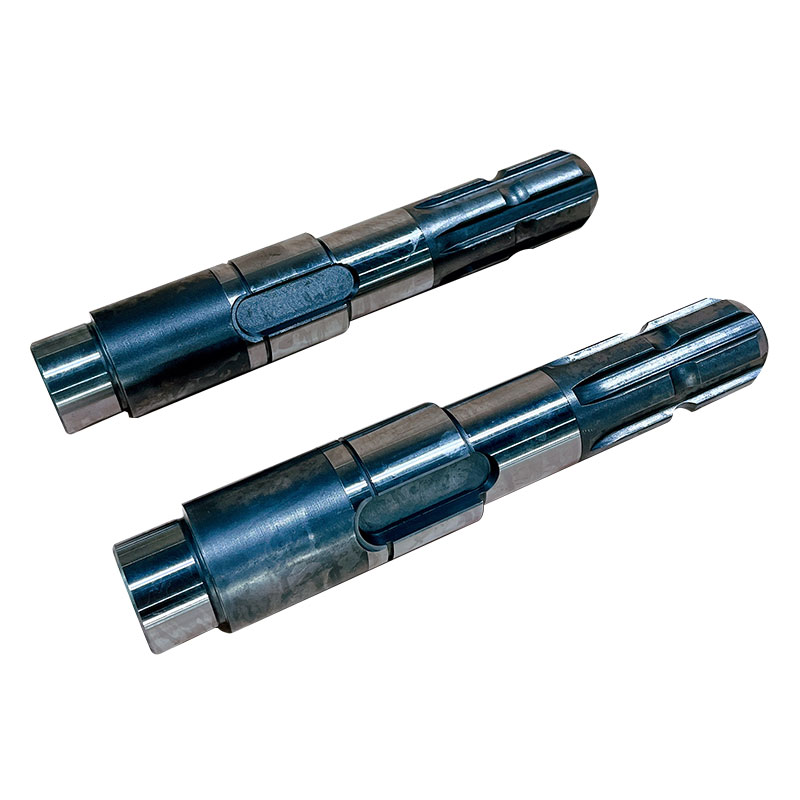
Input Shaft: The input shaft receives rotational power from the mower's engine or power take-off (PTO) system. It is connected to the gearbox's input gear, which initiates the power transmission process.
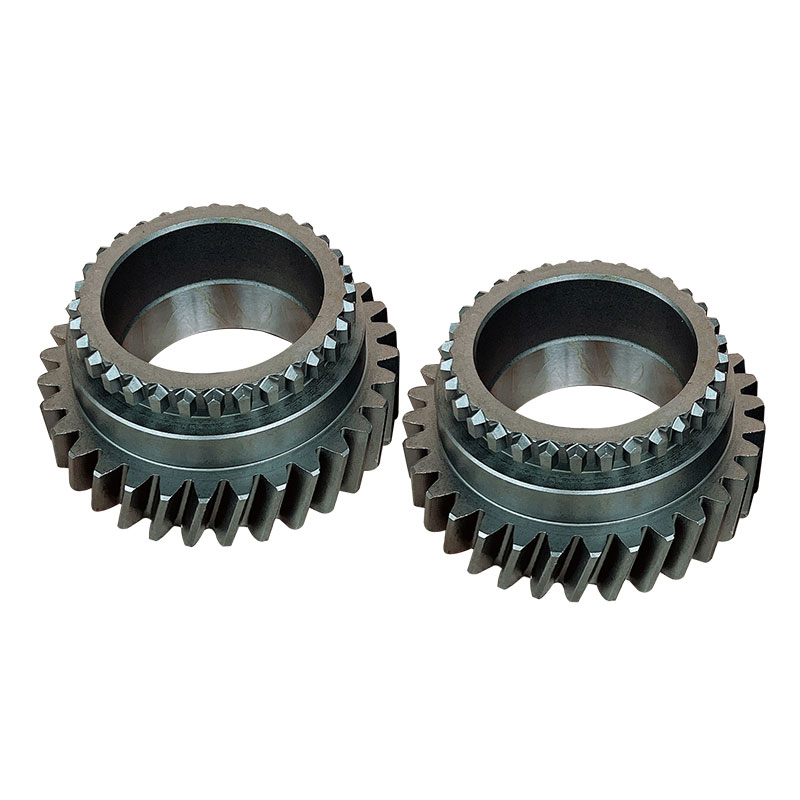
Gears: Inside the gearbox housing, a set of gears are arranged to transmit power from the input shaft to the output shaft. These gears may include spur gears, helical gears, or bevel gears, depending on the specific design of the gearbox. Gear ratios are carefully selected to optimize torque and speed for efficient cutting performance.
Output Shaft: The output shaft transfers power from the gearbox to the flail cutting mechanism. It is connected to the gearbox's output gear, which rotates at the desired speed to drive the flail blades or hammers.
Bearings: Bearings support and guide the rotating shafts and gears within the gearbox, reducing friction and wear. They are typically ball bearings or roller bearings designed to withstand radial and axial loads.
Seals and Gaskets: Seals and gaskets prevent lubricant leakage and ingress of contaminants into the gearbox, ensuring smooth operation and prolonging the lifespan of internal components.
Lubrication System: A lubrication system delivers oil or grease to the gearbox's moving parts, reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing premature wear and failure. Some gearboxes may have integrated oil reservoirs and pumps, while others rely on manual lubrication or external systems.

Keywords.
Cast Iron Flail Mower Gearbox
Heat-Treated Gears for Flail Mowers
Sealed Gearbox for Dusty Environments
Low RPM High Torque Flail Mower Gearbox
Weather-Resistant Verge Mower Gearbox
ISO-Certified Flail Mower Gear Drive
Long-Lasting Flail Mower Gearbox
Low Maintenance Gearbox for Verge Mowers
Overload Protection Flail Mower Gearbox
Quiet Gearbox for Municipal Mowing
Gearbox Repair for Flail Verge Mowers
Product video


















